

It does not correspond to any user ID in the web application and does not store any personally identifiable information. The cookie is used by cdn services like CloudFlare to identify individual clients behind a shared IP address and apply security settings on a per-client basis. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.
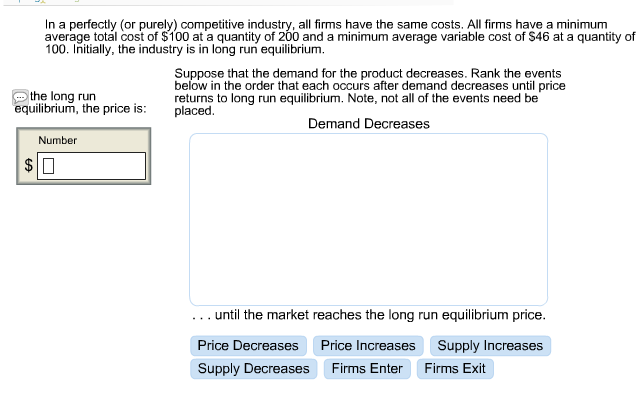 Farmers market with many farmers and buying selling vegetables. Some markets are close to perfect competition, for example The supply curve will fall until price rises back to a level which gives normal profit. Now firms would make a loss, and some will go out of business causing the supply curve to shift to the left. If there was a fall in market demand, the price would fall. With price at P1, profits are maximised at Q1 and normal profits are made once again (AR=AC). New firms enter (supply increases from S1 to S2) until the price falls to P1. However, the supernormal profit encourages more firms to enter the market. At Q2, (P, AR is greater than ATC) and therefore the firm now makes supernormal profit. A firms marginal cost (MC) curve is effectively its supply curve. Due to the rise in price to P2, profits are now maximised at Q2. Market demand rises from D1 to D2 causing the price to rise from P1 to P2. At this price firms make normal profits – because average revenue (AR) = average cost (AC)Ĭhanges in Perfect Competition equilibrium.
Farmers market with many farmers and buying selling vegetables. Some markets are close to perfect competition, for example The supply curve will fall until price rises back to a level which gives normal profit. Now firms would make a loss, and some will go out of business causing the supply curve to shift to the left. If there was a fall in market demand, the price would fall. With price at P1, profits are maximised at Q1 and normal profits are made once again (AR=AC). New firms enter (supply increases from S1 to S2) until the price falls to P1. However, the supernormal profit encourages more firms to enter the market. At Q2, (P, AR is greater than ATC) and therefore the firm now makes supernormal profit. A firms marginal cost (MC) curve is effectively its supply curve. Due to the rise in price to P2, profits are now maximised at Q2. Market demand rises from D1 to D2 causing the price to rise from P1 to P2. At this price firms make normal profits – because average revenue (AR) = average cost (AC)Ĭhanges in Perfect Competition equilibrium. 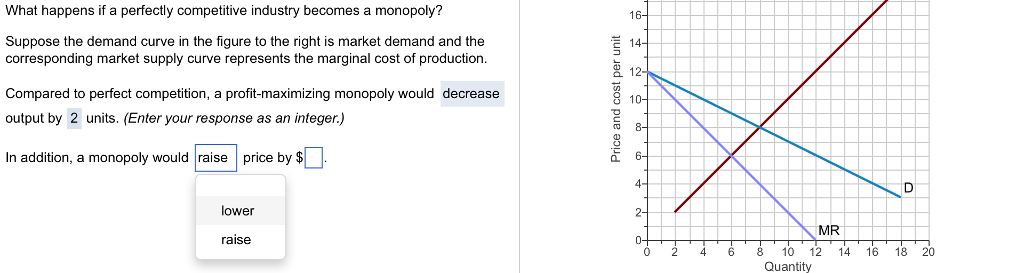
 A firm maximises profit at Q1 where MC = MR. Individual firms (on the left) are price takers. This sets the market equilibrium price of P1. The market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right). In the long-run firms in perfect competition will make normal profits. Therefore firms have an elastic demand curve. If they set a higher price, nobody would buy because of perfect knowledge. Firms are price takers this means their demand curve is perfectly elastic. The price is set by the industry supply and demand. Perfect competition is a market structure with:
A firm maximises profit at Q1 where MC = MR. Individual firms (on the left) are price takers. This sets the market equilibrium price of P1. The market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right). In the long-run firms in perfect competition will make normal profits. Therefore firms have an elastic demand curve. If they set a higher price, nobody would buy because of perfect knowledge. Firms are price takers this means their demand curve is perfectly elastic. The price is set by the industry supply and demand. Perfect competition is a market structure with:








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
